Probability Union And Intersection Examples Pdf

Now find the probability that the number rolled is both even and greater than two.
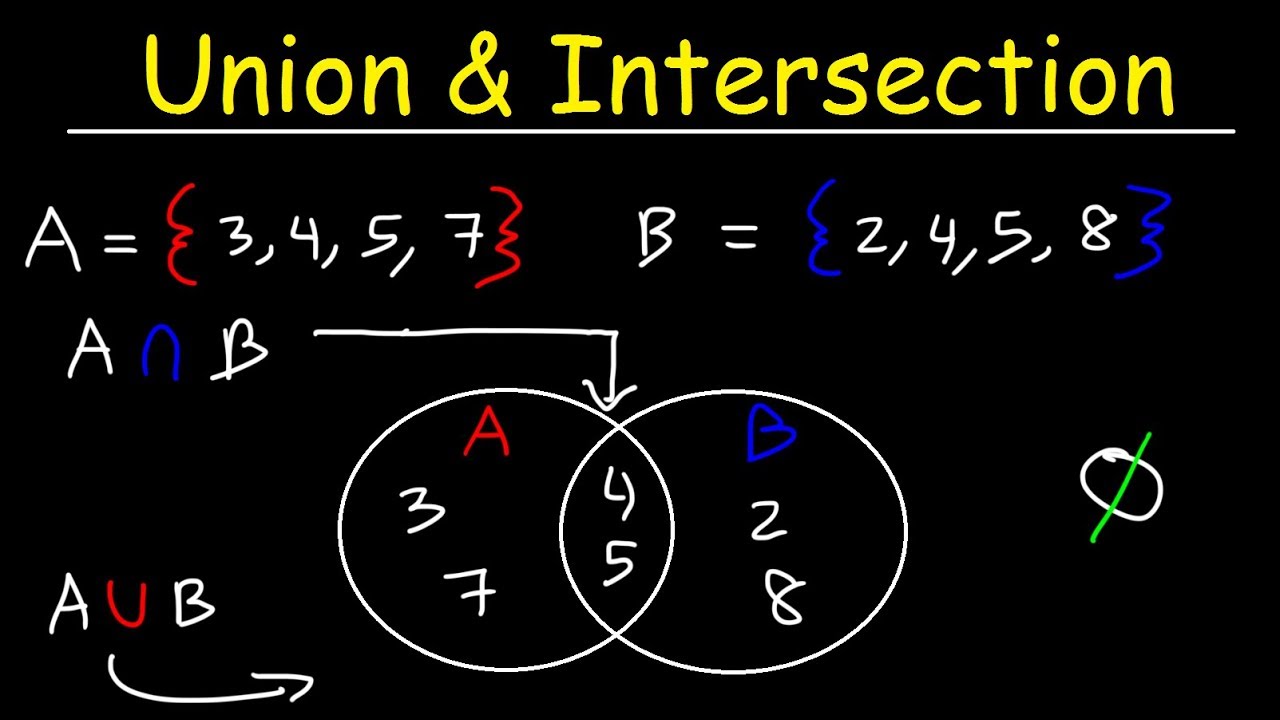
Probability union and intersection examples pdf. Probability of the union and the intersection of events probability of the union of events to compute the probability of the union of events we have to check whether they are compatible or incompatible. If events a and b are mutually exclusive p a b 0. To learn more about probability enrol in our full course now. Probability of union and intersection.
The probability of both events happening is 0 003. Examples for our first example suppose that we know the following values for probabilities. Only then is the probability of the union equal to the sum of probabilities of the event. The probability that events a or b occur is the probability of the union of a and b.
Let f be the probability of getting a flat tire. Https bit ly probabilitydm in this video we will learn. Some of the worksheets for this concept are unions and intersections work 3 unions and intersections answer key union intersection complement work pdf using venn diagrams to solve probability problems chapter 3 probability probability of compound events. The probability of the intersection of two events is an important number because it is the probability that both events occur.
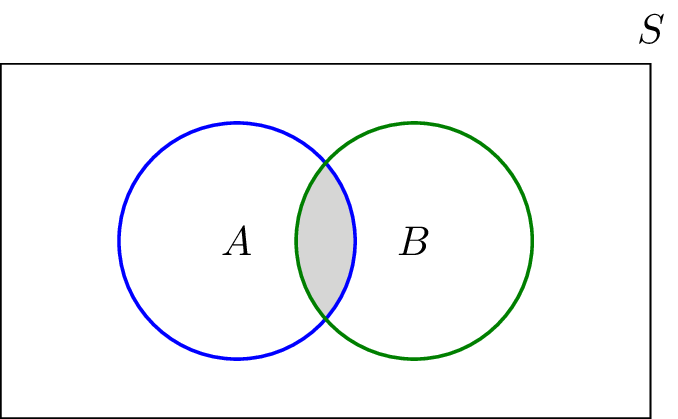
The probability of the intersection of events a and b is denoted by p a b. Suppose the die is fair. Summary of union vs. Intersection both union and intersection are the two fundamental operations through which sets can be combined and related to each other.
Find the probability that the number rolled is both even and greater than two. Then use the equation involving the union and intersection of two events. P a b 0 8 and p b 0 5. In terms of set theory union is the set of all the elements that are in either set or in both whereas intersection is the set of all distinct elements that belong to both the sets.
What is the probability that at least one of the events will happen on a particular day. Suppose the die has been loaded so that p 1 frac 1 12 p 6 frac 3 12 and the remaining four outcomes are equally likely with one another. Mathsf p a cup b mathsf p a mathsf p b otherwise if the events are not disjoint ie they have common outcomes then we would be over measuring and must exclude the measure of the intersection. Let r be the event of the windshield getting hit with a rock.